Class method overload resolution
非静态成员函数重载问题
除构造函数、析构函数、自定义转换函数外,类的非静态成员函数第一个参数都是隐式的类对象本身。而对象的类型,决定了成员函数的重载。调用成员函数时,对象本身由三个维度确定具体类型:const与non-const, 左值与右值,引用与非引用,这些对象的实际类型与成员方法的定义类型,最终决定了重载方式。这个问题实则复杂,若要更精细的管理类的行为,有必要弄清楚详细的重载细则。本文试图在实验结果的基础上理清楚这个问题。
三个原则:
- 方法重载的优先级。C++标准为各种成员方法的重载规定了
fallback,这些fallback的行为增加了问题的复杂程度。同一个对象可以重载带不同修饰符的方法,区别在于优先级不同,本文也会搞清楚重载的优先级。 - 引用修饰符不能与不带引用修饰符的方法重载。一个类的方法要么带引用修饰符
&,或者&&,要么不带任何引用修饰符,二者不能共存;带&和&&的同名方法可以重载。 - 非常量修饰的方法无法被任何常量修饰的对象调用。
const修饰的方法可能被普通对象调用,反之不成立。
无引用修饰符
无引用修饰符的情况下只有const和非const两种情况:
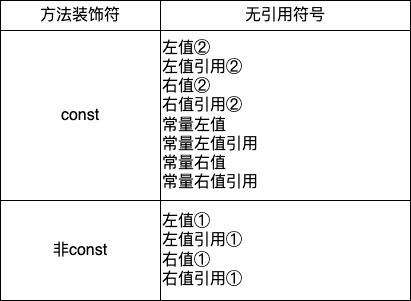
- 图中标号为重载时的优先级
const修饰的方法由于无法修改成员,当无非const的重载方法时,可以被普通非const对象调用;反之则不成立- 在无引用修饰符的情况下,方法都可以被右值或者右值引用对象调用
有引用修饰符
有引用修饰符情况要更加复杂:
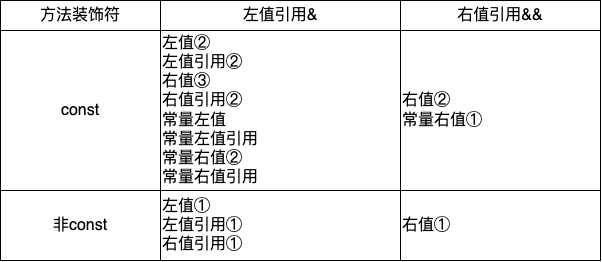
这个表中有几点要说明:
- 图中标号代表重载的优先级
- 带右值引用修饰符的方法只能被右值调用
- 所有的引用 都是左值,所有的引用都会重载到左值修饰符的方法上
const与const&修饰的方法对比
这两种方法是能被最大多数类型的对象重载的方法。如果仅有其中的一个,那么他们的功能相同;其他方法都是缩小范围的,或者重载优先级更高,也意味着使用范围更窄
Code Example
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
// 成员非静态方法重载时要考虑const, non-const, ref-qualified,
// non-ref-qualified。 类本身作为第一个参数(implicit object parameter),
// 以下简称IOP. 注意: constructor、destructor、conversion function没有
// implicit object parameter,所以不能使用const或者ref-qualifier.
//
// 带ref-qualifer与不带ref-qualifer的同名方法不能共存,带ref-qualifier的方法
// 与不带ref-qualifier的方法不能相互重载,这包括带const和不带const的所有方法。
//
// 默认情况下,所有implicit object member
// function(https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/language/member_functions)
// 都需要考虑const-qualifier|non-const-qualifier,
// non-ref-qualifer|(rvalue-ref-qualifier, lvalue-ref-qualifier),
// 共计:2x1+2x2=6种情况:
//
// A. non-const-qualifier:
// - IOP必须是non-const传入
// #1. 不带ref-qualifer的方法:
// - IOP可以是左值(引用),右值(引用)
// - 带ref-qualifer的方法,则:
// #2.带&,则IOP只能以左值(引用),右值引用(右值引用没有完美转发,看作左值)
// #3. 带&&,则IOP只能以右值传入; 注意右值引用传入后被视为左值
//
// B. const-qualifier:
// #4. 不带ref-qualifer:
// -
// IOP可以是常量左值(引用),非常量左值(引用),非常量右值(引用),也可以是常量右值,常量右值引用
// (常量右值引用没有完美转发,则被看作左值)
// - 带ref-qualifier的方法,则:
// #5.带&,则IOP以常量左值(引用)、非常量左值(引用)、常量右值,常量右值引用(常量右值引用没有完美转发,
// 则被看作左值),非常量右值引用,非常量右值(以上右值和右值引用重载优先级低于#6)
// #6.带&&,则IOP以非常量右值,常量右值传入;重载优先级高于#5;注意右值引用传入后被视为左值
// 重要:常量右值引用是個左值;
class MemoryBlock
{
public:
/// can not overload by ref-qualifier
void non_const_non_ref_cant_overload()
{
std::cout << __LINE__ << " Non const non ref method called" << std::endl;
}
/// Cannot overload a member function with ref-qualifier '&' with a member
/// function without a ref-qualifierclang(ref_qualifier_overload)
// void non_const_non_ref_cant_overload() &{
// std::cout << "Non const non ref method called" << std::endl;
// }
/// Cannot overload a member function with ref-qualifier '&&' with a member
/// function without a ref-qualifierclang(ref_qualifier_overload
// void non_const_non_ref_cant_overload() && {
// std::cout << "Non const non ref method called" << std::endl;
// }
void non_const_can_overload() &
{
std::cout << __LINE__ << " Non const lvalue ref method called" << std::endl;
}
void non_const_can_overload() &&
{
std::cout << __LINE__ << " Non const rvalue ref method called" << std::endl;
}
void const_cant_overload() const
{
std::cout << __LINE__ << " Const non ref method called" << std::endl;
}
/// Cannot overload a member function with ref-qualifier '&' with a member
/// function without a ref-qualifierclang(ref_qualifier_overload)
// void const_cant_overload() const& {
// std::cout << "Const non ref method called" << std::endl;
// }
/// Cannot overload a member function with ref-qualifier '&&' with a member
/// function without a ref-qualifierclang(ref_qualifier_overload)
// void const_cant_overload() const&& {
// std::cout << "Const non ref method called" << std::endl;
// }
void const_can_overload() const&
{
std::cout << __LINE__ << " Const lvalue ref method called" << std::endl;
}
void const_can_overload() const&&
{
std::cout << __LINE__ << " Const rvalue ref method called" << std::endl;
}
};
// Class and Array type can have const qualified rvalue in C++, this can be created
// by function return a const qualified class or array type
// https://timsong-cpp.github.io/cppwp/n4861/expr.type#2
const MemoryBlock create_const_rvalue()
{
const MemoryBlock cm = MemoryBlock();
return cm;
}
int main()
{
std::cout << "<<<< #1 <<<<" << std::endl;
MemoryBlock m;
/// #1: ok, non-const lvalue
m.non_const_non_ref_cant_overload();
/// #1: ok, non-const rvalue
MemoryBlock().non_const_non_ref_cant_overload();
MemoryBlock& mr = m;
/// #1: ok, lvalue reference
mr.non_const_non_ref_cant_overload();
MemoryBlock&& m_rvalue_ref = MemoryBlock();
// #1: ok, rvalue reference
m_rvalue_ref.non_const_non_ref_cant_overload();
const MemoryBlock cm;
/// A: nok, only accept non const
// cm.non_const_non_ref();
// const MemoryBlock&& cmr=std::move(m);
/// A: nok, only accept non const
// cmr.non_const_non_ref();
// A: nok, only accept non const
// create_const_rvalue().non_const_non_ref_cant_overload();
std::cout << "<<<< #2 <<<<" << std::endl;
MemoryBlock n;
/// #2: ok, non const lvalue, overload void non_const_can_overload() &, if
/// only define void non_const_can_overload() &&, there will be overload
/// failure
n.non_const_can_overload();
MemoryBlock& n_lvalue_ref = n;
/// #2: ok, non const lvalue reference
n_lvalue_ref.non_const_can_overload();
/// #2: ok, non const rvalue reference
MemoryBlock&& n_rvalue_ref = MemoryBlock();
n_rvalue_ref.non_const_can_overload();
std::cout << "<<<< #3 <<<<" << std::endl;
/// #3: ok, non const rvalue, overload void non_const_can_overload() &&, if
/// only define void non_const_can_overload() &, there will be overload
/// failure
MemoryBlock().non_const_can_overload();
/// A: nok, only accetp non const
/// cm.non_const_can_overload();
std::cout << "<<<< #4 <<<<" << std::endl;
/// #4: ok, non-const lvalue
m.const_cant_overload();
/// #4: ok, non-const lvalue reference
mr.const_cant_overload();
/// #4: ok, const lvalue
cm.const_cant_overload();
const MemoryBlock& cons_lvalue_ref = m;
/// #4: ok, const lvalue reference
cons_lvalue_ref.const_cant_overload();
/// #4: ok, non-const rvalue
MemoryBlock().const_cant_overload();
MemoryBlock&& non_const_rvalue_ref = MemoryBlock();
/// #4: ok, non const rvalue reference
non_const_rvalue_ref.const_cant_overload();
const MemoryBlock&& cmr = MemoryBlock();
/// #4: ok, const rvalue reference is lvalue, except using std::forward
cmr.const_cant_overload();
// #4: ok, const rvalue
create_const_rvalue().const_cant_overload();
std::cout << "<<<< #5 <<<<" << std::endl;
/// #5: ok, const lvalue, overload void const_can_overload() const&, if only
/// define void const_can_overload() const&&, there will be overload failure
cm.const_can_overload();
/// #5: ok, const lvalue reference
cons_lvalue_ref.const_can_overload();
/// #5: ok, non const lvalue reference
n_lvalue_ref.const_can_overload();
/// #5: ok, non const lvalue
m.const_can_overload();
/// #5: ok, const rvalue reference is lvalue, except using std::forward
cmr.const_can_overload();
/// #5: ok, non const rvalue reference
non_const_rvalue_ref.const_can_overload();
// #5: ok, but overload priority lower than #6, can be testfied by comment out #6 method
create_const_rvalue().const_can_overload();
std::cout << "<<<< #6 <<<<" << std::endl;
/// #6: ok, non const rvalue;overload void const_can_overload() const&&, if
/// void const_can_overload() const&& is not defined, void
/// const_can_overload() const& will be overloaded,since const lvalue
/// reference can bind to rvalue
MemoryBlock().const_can_overload();
// #6: ok, const rvalue
create_const_rvalue().const_can_overload();
}