Docker CLI
参考文章
-
这篇文章对tty的解释非常到位,可以说是最有价值的关于tty的文章
-
Using pseudo-terminals (pty) to control interactive programs
这篇主要提供了tty的编程代码
-
修改文件描述符
-
pipe管道IPC通信
操作系统支持
如果想理解Docker CLI与Docker Daemon的交互,必须了解底层操作系统的支持
dup2修改文件描述符
Linux操作系统下可以使用dup复制文件描述符,可以使用dup2来修改文件描述符的指向:
#include <chrono>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <ostream>
#include <string>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <thread>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MAX_BUFFER_SIZE 1024
std::string readLineFromFd(int fd) {
char buff[MAX_BUFFER_SIZE - 1];
memset(buff, 0, MAX_BUFFER_SIZE - 1);
char c;
int cnt = 0;
while (read(fd, &c, 1) && cnt != MAX_BUFFER_SIZE - 2) {
if (c == '\n') {
return std::string(buff);
} else {
buff[cnt] = c;
++cnt;
}
}
// EOF
return std::string(buff);
}
int main() {
while (true) {
std::cout << "Enter a command or filename:";
fflush(stdout);
/// std::cout when connect to tty is line buffered; otherwise is full
/// buffered std::cin and std::cerr will flush std::cout automatically
/// getline will read until '/n', '/n' will be extracted, but not stored
auto line = readLineFromFd(STDIN_FILENO);
if (line.size() == 0) {
exit(0);
}
std::cout << "You entered: " << line << std::endl;
// If input is *.input, open the file and print every line
if (line.find(".input") != std::string::npos) {
auto file = open(line.c_str(), O_RDONLY);
if (file == -1) {
std::cerr << "Error opening file"
<< " Error code:" << file << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
// Redirect stdin to the file
int original_stdin = dup(STDIN_FILENO);
dup2(file, STDIN_FILENO);
close(file);
// Print every line
std::string line = readLineFromFd(STDIN_FILENO);
while (true) {
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
if (line == "ChangeStdinToTerminal") {
// Switch stdin back to terminal
if (dup2(original_stdin, STDIN_FILENO) == -1) {
exit(1);
};
close(original_stdin);
break;
}
std::cout << line << std::endl;
line = readLineFromFd(STDIN_FILENO);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
tty虚拟终端
操作系统内核提供的虚拟终端支持,以下代码来zhttp://www.rkoucha.fr/tech_corner/pty_pdip.html:
/// demo from :http://www.rkoucha.fr/tech_corner/pty_pdip.html
#define _XOPEN_SOURCE 600
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define __USE_BSD
#include <termios.h>
int main(void) {
int fdm, fds, rc;
char input[150];
fdm = posix_openpt(O_RDWR);
if (fdm < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error %d on posix_openpt()\n", errno);
return 1;
}
rc = grantpt(fdm);
if (rc != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error %d on grantpt()\n", errno);
return 1;
}
rc = unlockpt(fdm);
if (rc != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error %d on unlockpt()\n", errno);
return 1;
}
// Open the slave PTY
fds = open(ptsname(fdm), O_RDWR);
// Creation of a child process
if (fork()) {
// Father
// Close the slave side of the PTY
close(fds);
while (1) {
// Operator's entry (standard input = terminal)
write(1, "Input : ", sizeof("Input : "));
rc = read(0, input, sizeof(input));
if (rc > 0) {
// Send the input to the child process through the PTY
write(fdm, input, rc);
// Get the child's answer through the PTY
rc = read(fdm, input, sizeof(input) - 1);
if (rc > 0) {
// Make the answer NUL terminated to display it as a string
input[rc] = '\0';
fprintf(stderr, "%s", input);
} else {
break;
}
} else {
break;
}
} // End while
} else {
struct termios slave_orig_term_settings; // Saved terminal settings
struct termios new_term_settings; // Current terminal settings
// Child
// Close the master side of the PTY
close(fdm);
// Save the default parameters of the slave side of the PTY
rc = tcgetattr(fds, &slave_orig_term_settings);
// Set raw mode on the slave side of the PTY
new_term_settings = slave_orig_term_settings;
cfmakeraw(&new_term_settings);
tcsetattr(fds, TCSANOW, &new_term_settings);
// The slave side of the PTY becomes the standard input and outputs of the
// child process
close(0); // Close standard input (current terminal)
close(1); // Close standard output (current terminal)
close(2); // Close standard error (current terminal)
dup(fds); // PTY becomes standard input (0)
dup(fds); // PTY becomes standard output (1)
dup(fds); // PTY becomes standard error (2)
while (1) {
rc = read(fds, input, sizeof(input) - 1);
if (rc > 0) {
// Replace the terminating \n by a NUL to display it as a string
input[rc - 1] = '\0';
printf("Child received : '%s'\n", input);
} else {
break;
}
} // End while
}
return 0;
} // main
pipe管道IPC通信
Linux操作系统支持使用管道的IPC通信:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define BUFFER_SIZE 25
int main() {
int pipefd[2];
pid_t pid;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
// Create pipe
if (pipe(pipefd) == -1) {
perror("pipe");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// Fork a child process
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (pid == 0) { // Child process
close(pipefd[1]); // Close the write end of the pipe
// Read from the pipe
printf("Child process reading from the pipe...\n");
read(pipefd[0], buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
printf("Child process received: %s\n", buffer);
close(pipefd[0]); // Close the read end of the pipe
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
} else { // Parent process
close(pipefd[0]); // Close the read end of the pipe
// Write to the pipe
printf("Parent process writing to the pipe...\n");
write(pipefd[1], "Hello from parent!", 18);
close(pipefd[1]); // Close the write end of the pipe
wait(NULL); // Wait for the child process to finish
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
return 0;
}
Docker CLI工作原理
在了解了底层操作系统的支持后,下面是我整理画出的Docker CLI与容器的交互过程(不保证正确):
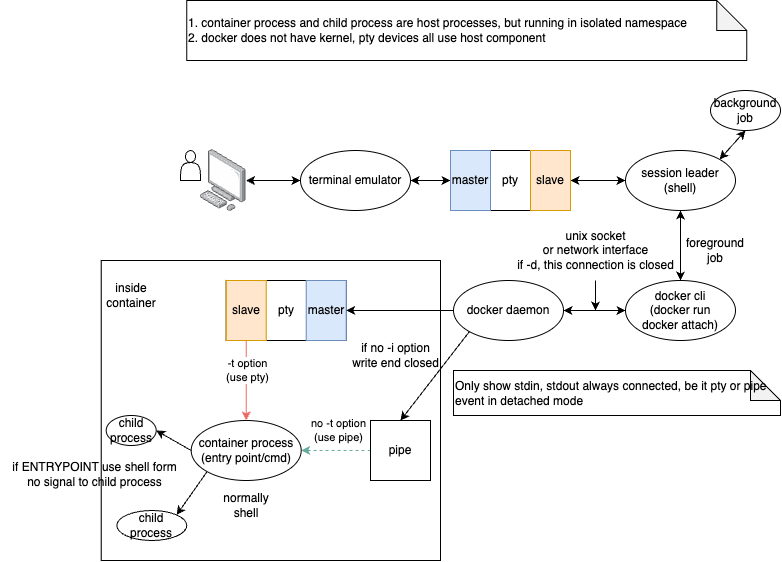
说明如下:
- 当运行Docker CLI程序,例如
docker run,docker attach等,这些程序会跟Docker Daemon通信;Docker CLI与Docker Daemon是客户/服务的工作模式 - Docker CLI与Docker Daemon的通信可以使用本机的unix domain socket,也可以是远程的网络连接,比如TCP等
- 真正的容器操作,例如创建运行容器、attach容器、关闭容器等操作都是由Docker Daemon完成的,所以Docker Daemon是整个Docker系统的核心组件
- 当使用
docker run-d选项运行一个镜像时,Docker CLI与Docker Daemon之间的连接被关闭,Docker CLI程序执行完毕,但是运行的容器跟这个选项没有任何关系,用户随时可以使用docker attach命令来重新与Docker Daemon建立连接 - Docker Daemon与创建的容器进程(运行在与Host独立的namespace中)之间的通信可以是
pipe,也可以是tty。Docker Daemon通过这些通信手段来控制容器进程的标准输入 - 当使用
docker run-t,选项时,会为容器进程分配一个tty,注意这个tty是Host内核中的tty,但是工作在容器进程这个独立与Host 的namespace中 - 如果不使用
-t,则会直接使用pipe与容器进程通信 - 如果使用
docker run-i,则是告诉Docker Daemon保持容器进程的标准输入为打开状态,即不关闭tty或者pipe的写入端 - 如果不使用
-i,则Docker Daemon会关闭tty或者pipe的写入端,如此容器进程的程序会在标准输入读到EOF