Parameter binding
绑定矩阵(binding matrix)
假设:
- 类型
T为定义了所有特殊成员函数的的类型 - 表格左侧为形参类型
- 表格上方为实参expression,及对应的type, value category
则C++有如下的绑定矩阵,且绑定时的动作如下:
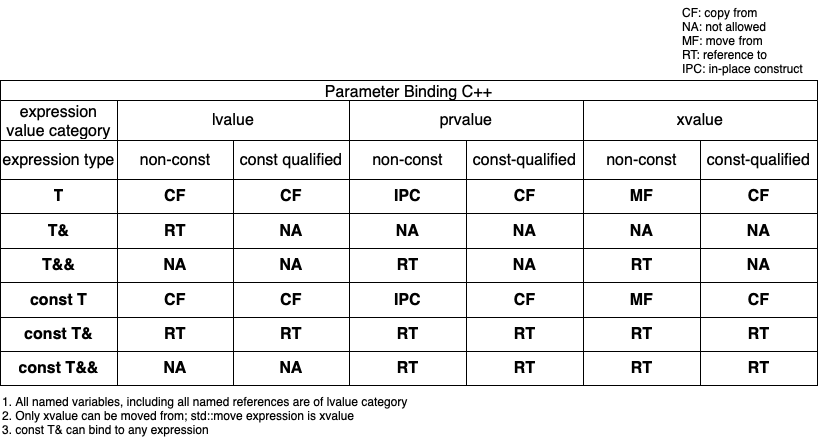 |
|---|
| Parameter Binding in C++ |
说明:
- 当传入non-const xvalue构造一个对象时,如果没有定义移动构造函数,则会默认调用拷贝构造函数
- 以上表格中默认T类型定义了所有的类特殊成员函数
- 所有有名的变量,包括右值引用都是左值,所以不能传递给接收右值引用的入参类型!!
- 所有引用都是有名称的左值
- 函数调用参数传递分两步:
- 形参要通过binding绑定实参
- 无论函数形参是哪种类型,在函数内部,形参都被作为左值使用,如果要保留形参类型,必须使用std::forward转发
示例代码
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
struct Example {
// constructor
Example() { std::cout << "Example constructor" << std::endl; }
// destructor
~Example() { std::cout << "Example destructor" << std::endl; }
// copy constructor
Example(const Example &e) {
std::cout << "Example copy constructor" << std::endl;
}
// copy assignment operator
Example &operator=(const Example &e) {
std::cout << "Example copy assignment operator" << std::endl;
return *this;
}
// move constructor
Example(Example &&e) { std::cout << "Example move constructor" << std::endl; }
// move assignment operator
Example &operator=(Example &&e) {
std::cout << "Example move assignment operator" << std::endl;
return *this;
}
};
// write a function, that takes a parameter by value
void func(Example e) { std::cout << "func" << std::endl; }
// write a function, that takes a parameter by lvalue reference
void func_lref(Example &e) {
std::cout << "func lvalue reference" << std::endl;
}
// write a function, that takes a parameter by rvalue reference
void func_rref(Example &&e) {
std::cout << "func rvalue reference" << std::endl;
}
// function that takes a const value
void func_const(const Example e) { std::cout << "func const" << std::endl; }
// function that takes a const lvalue reference
void func_const_lref(const Example &e) {
std::cout << "func const lvalue reference" << std::endl;
}
// function that takes a const rvalue reference
void func_const_rref(const Example &&e) {
std::cout << "func const rvalue reference" << std::endl;
}
// test func, to pass various types of objects into it
void test_func() {
Example e;
Example &e_ref = e;
func(e); // lvalue
func(Example()); // rvalue
func(e_ref); // lvalue reference
Example &&e_rref = Example();
func(e_rref); // rvalue reference
const Example e_const;
func(e_const); // const lvalue
func(static_cast<const Example>(Example())); // const rvalue
const Example &e_const_ref = e;
func(e_const_ref); // const lvalue reference
const Example &&e_const_rref = Example();
func(e_const_rref); // const rvalue reference
}
// test func_lref, to pass various types of objects into it
void test_func_lref() {
Example e;
Example &e_ref = e;
func_lref(e); // lvalue
// func_lref(Example()); // rvalue
func_lref(e_ref); // lvalue reference
Example &&e_rref = Example();
func_lref(e_rref); // rvalue reference
const Example e_const;
// func_lref(e_const); // const lvalue
// func_lref(static_cast<const Example>(Example())); // const rvalue
const Example &e_const_ref = e;
// func_lref(e_const_ref); // const lvalue reference
const Example &&e_const_rref = Example();
// func_lref(e_const_rref); // const rvalue reference
}
// test func_rref, to pass various types of objects into it
void test_func_rref() {
Example e;
Example &e_ref = e;
// func_rref(e); // lvalue
func_rref(Example()); // rvalue
// func_rref(e_ref); // lvalue reference
Example &&e_rref = Example();
/// !! WARN: every named variable is lvalue, so it can't be passed to rvalue
/// reference
// func_rref(e_rref); // rvalue reference
const Example e_const;
// func_rref(e_const); // const lvalue
// func_rref(static_cast<const Example>(Example())); // const rvalue
const Example &e_const_ref = e;
// func_rref(e_const_ref); // const lvalue reference
const Example &&e_const_rref = Example();
// func_rref(e_const_rref); // const rvalue reference
}
// test func_const, to pass various types of objects into it
void test_func_const() {
Example e;
Example &e_ref = e;
func_const(e); // lvalue
func_const(Example()); // rvalue
func_const(e_ref); // lvalue reference
Example &&e_rref = Example();
func_const(e_rref); // rvalue reference
const Example e_const;
func_const(e_const); // const lvalue
func_const(static_cast<const Example>(Example())); // const rvalue
const Example &e_const_ref = e;
func_const(e_const_ref); // const lvalue reference
const Example &&e_const_rref = Example();
func_const(e_const_rref); // const rvalue reference
}
// test func_const_lref, to pass various types of objects into it
void test_func_const_lref() {
Example e;
Example &e_ref = e;
func_const_lref(e); // lvalue
func_const_lref(Example()); // rvalue
func_const_lref(e_ref); // lvalue reference
Example &&e_rref = Example();
func_const_lref(e_rref); // rvalue reference
const Example e_const;
func_const_lref(e_const); // const lvalue
func_const_lref(static_cast<const Example>(Example())); // const rvalue
const Example &e_const_ref = e;
func_const_lref(e_const_ref); // const lvalue reference
const Example &&e_const_rref = Example();
func_const_lref(e_const_rref); // const rvalue reference
}
// test func_const_rref, to pass various types of objects into it
void test_func_const_rref() {
Example e;
Example &e_ref = e;
// func_const_rref(e); // lvalue
func_const_rref(Example()); // rvalue
// func_const_rref(e_ref); // lvalue reference
Example &&e_rref = Example();
// func_const_rref(e_rref); // rvalue reference
const Example e_const;
// func_const_rref(e_const); // const lvalue
func_const_rref(static_cast<const Example>(Example())); // const rvalue
const Example &e_const_ref = e;
// func_const_rref(e_const_ref); // const lvalue reference
const Example &&e_const_rref = Example();
// func_const_rref(e_const_rref); // const rvalue reference
}
int main() {
test_func();
test_func_lref();
test_func_rref();
test_func_const();
test_func_const_lref();
test_func_const_rref();
return 0;
}