Mapping design pattern in storage management
It’s fun to observe and generalize the similarities between different systems. In computer storage, the virtual memory design in RAM management and the logical block design in mass storage management shares the same pattern: mapping of logical/virtual memory to physical memory.
Reference: Managed Flash Background Operations Series
virtual address to physical address mapping in RAM management
In order for a process to have continuous memory address and to have bigger address space than actual size of the RAM, virtual memory is invented. We are not focusing on the techniques about how virtual memory works here, instead we are comparing similarities. Following points need to be noted:
- kernel manages processes and their virtual tables, which mapps virtual memory to physical memories
- kernel manages physical memories and is responsible for the algorithm for how the physical memory is used, such as which page is swapped out(page replacement algorithm); and how many physical memory is allocated to each process(allocation algorithm)
- user program decides, at runtime, which physical memory will be accessed
- user program have continuous address space
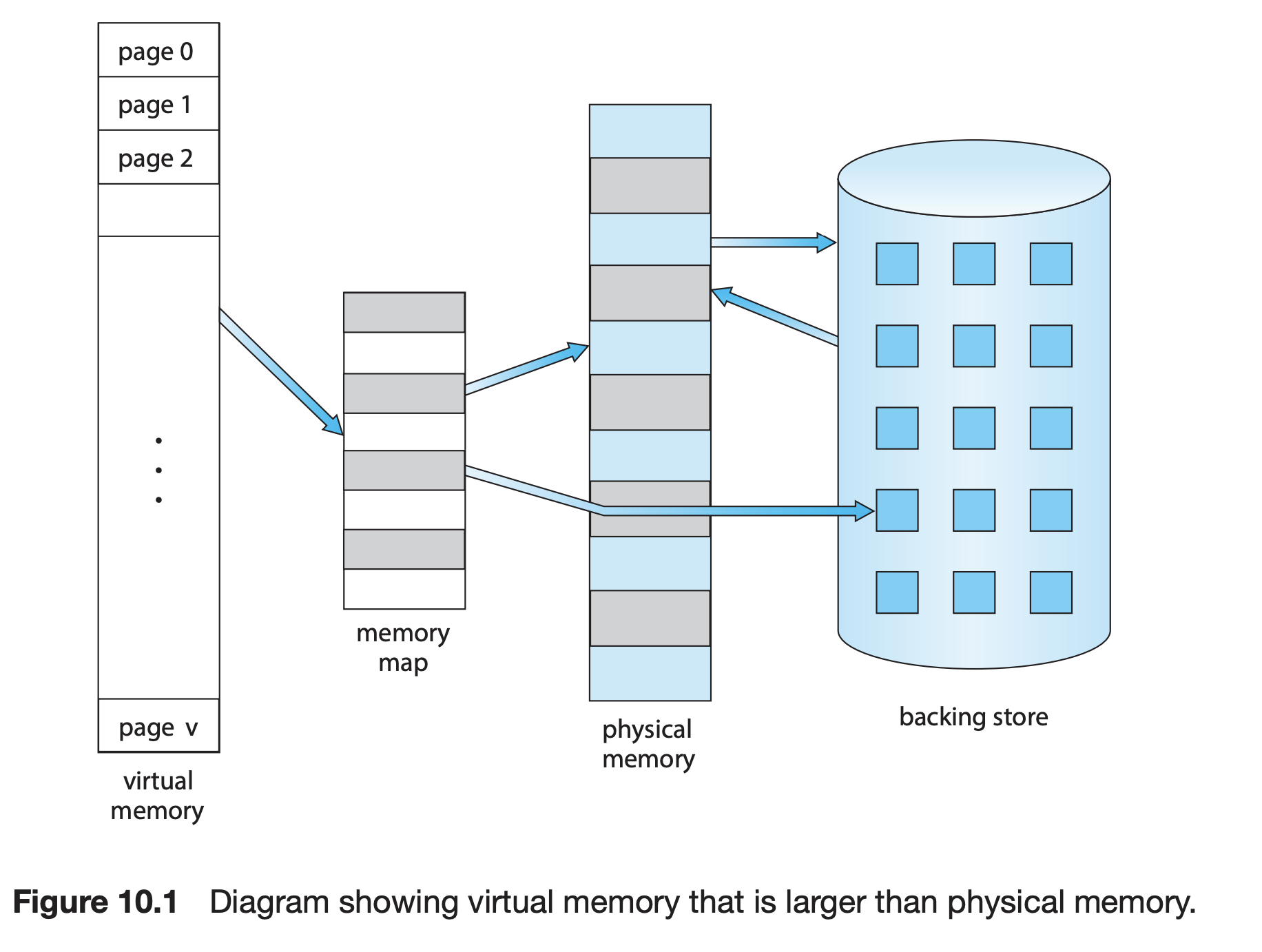 |
|---|
| Operating system concepts / Abraham Silberschatz |
logical block to physical block mapping in mass storage management
In order for the kernel to have continuous storage block access, the storage controller maintains a logical block address to physical block address mapping table. Following points need to be noted:
- storage device controller mantains the mapping table from logical block address to physical block address
- kernel use the logical block address as continuous blocks
- storage device is responsible for allocation and reallocation a logical block to a physical block
- kernel decides when to use the logical block, such as when creating files, and is reponsible for optimization for accessing logical blocks, for example, kernel might use algorithm to read adjacent logical blocks sequentially so that the seek operation is more efficient for the device controller; kernel is also responsible to reduce fragmentation in the use of the logical address space
- storage device is responsible for garbage collection and wear leveling of the physical blocks and might assign different physical block address for the same logical block(kernel knows nothing about this)
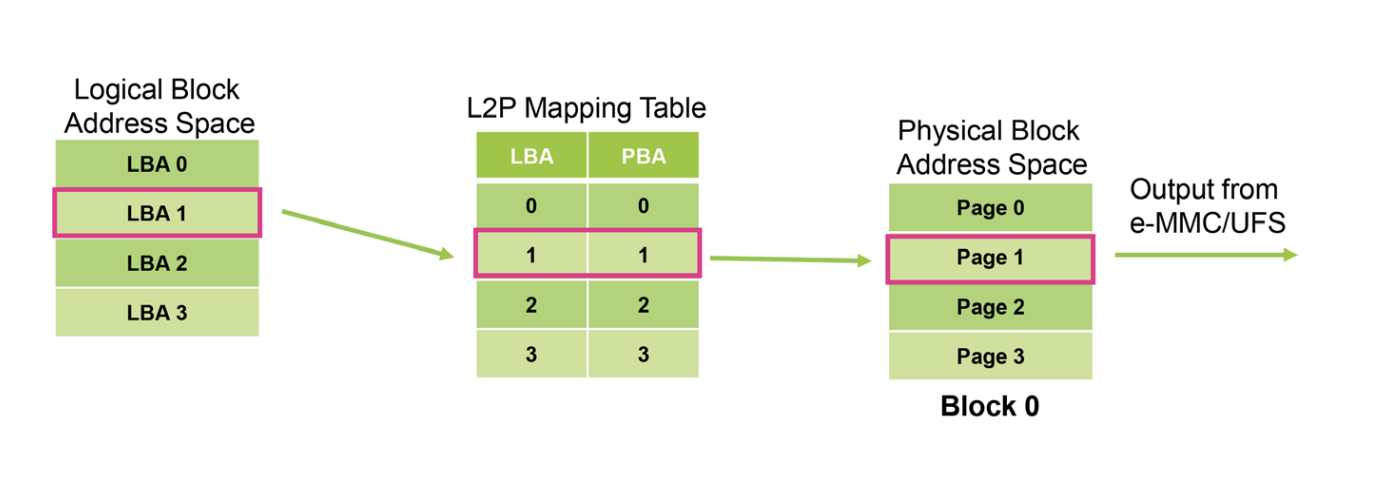 |
|---|
| Logical block addressing and metadata mapping within NAND flash memory |
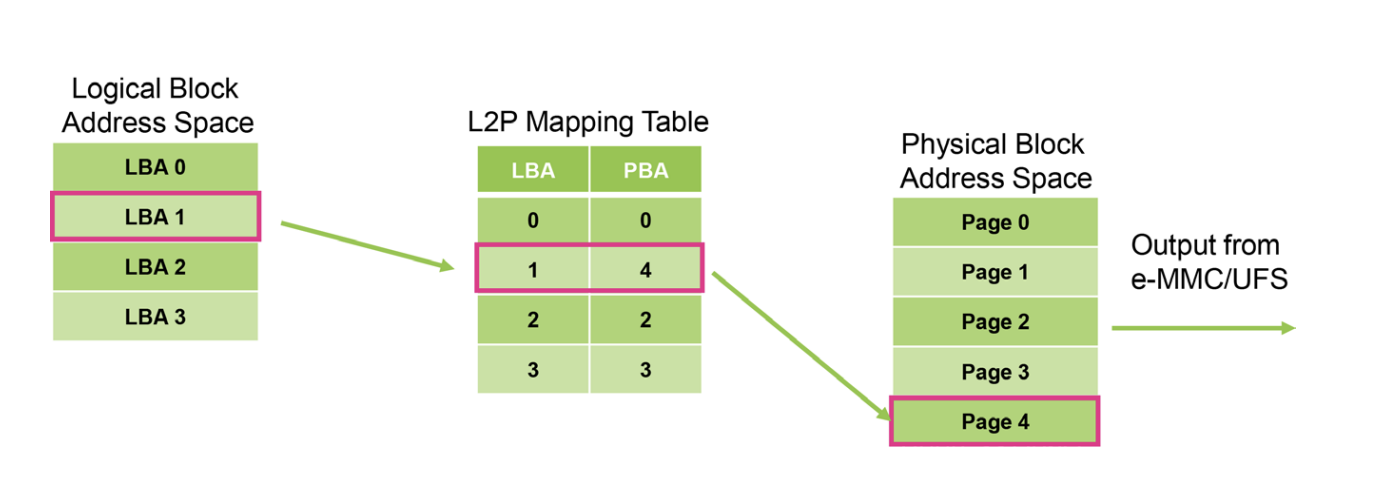 |
|---|
| Logical block addresses seen by the host do not change even after the physical block address space changed |
philosophy of detaching physical from logical
The ideology behind virtual memory design and the logical block address design is the same: detach logical memory from physical memory, through the use of mapping table:
- physical memory can be mapped to multi logical/virtual memory, thus shared by them
- logical/virtual memory is continuous, while the actual storage in physical memory is not. This is a huge advantage, since physical memory unit might be corrupted. With the help of mapping table, the corrupted memory unit can be remapped to a good one and the logical memory need not to know anything about it
It is indeed true that:
“We can solve any problem by introducing an extra level of indirection.”